-
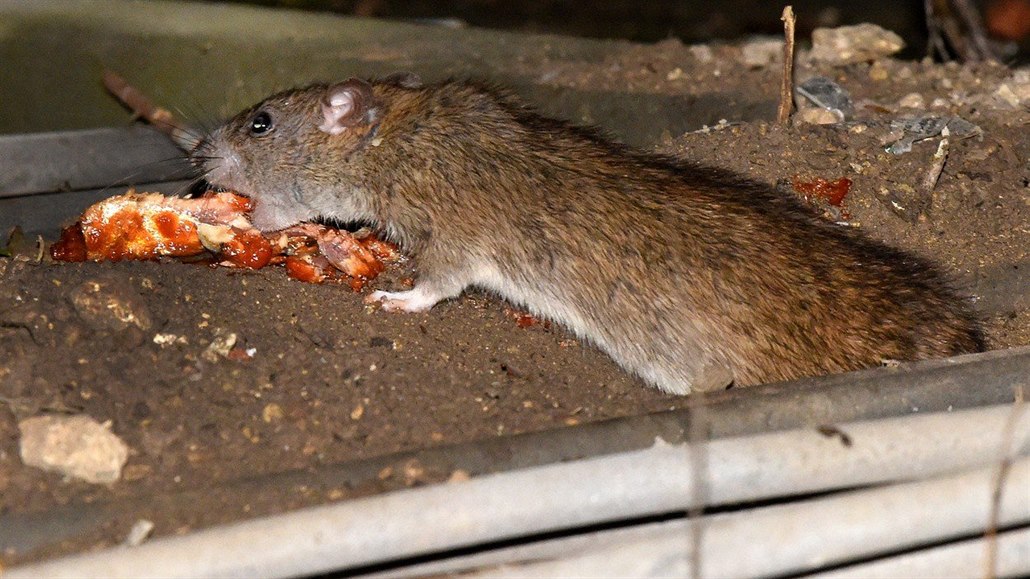
In human metropolises, they find a lot of food and countless safe cover. They are a very hospitable home for them. And quickly in many. It is estimated that there are at least three weeks in rats and rats, not rats. And their number is growing rapidly.
-
In human metropolises, they find a lot of food and countless safe cover. They are a very hospitable home for them. And quickly in many. It is estimated that there are at least three weeks in rats and rats, not rats. And their number is growing rapidly.
 |
The global human population is growing in cities at a rapid rate, and by 2050 it should be within the metropolis and 70 percent of the planet’s population. But they will not be there alone. The crowded urban dungles have chosen other species for their lives, which have been followed by hunters for centuries. Rats and rats. Even their sweats increase sharply due to favorable conditions.
For decades, the people have been waging a futile struggle with them, which they are now beginning to lose. Theoretically, under normal conditions, 482 million rodents can grow from one strip of rats over the course of three years. The only question is when we start to get closer to those special conditions for the popular growth of rodents. Experts answer that first.
City status for rodents
It would be easy to seduce it into climate change, to rodentologist Bobby Corrigan. Undoubtedly, they play a role in the unprecedented number of rats, but they have problems on several levels. And it is only in general that it is necessary to emphasize that the urban environment of rodents is maximally suitable.
Cities, and in Europe, Asia, or the United States, represent a simple table for rodents. Food, in the form of piles of garbage, open baskets and accessible containers, is on every corner. There are large nestens to store food and raw materials to make food, translate and docks full of various delicacies.
Tern city is enough lazy, so rats and rats have no problem finding a safe cover for starting a family and bringing out young. Each metropolis has a safe covered corridor, which these invites can use for their movements, without being threatened by any predator. Cities are built for humans in terms of architecture and engineering, but rodents can do a lot of them, Corrigan said.
Winter is not clear
After years, a dynamic equilibrium was established, which could be slightly tilted in favor of rats and rats. Their change involved a variety of practical technical measures, from regular sewerage, from the frequency of waste collection to direct rodent control. And it was mainly the winter that slowed their popular growth.
Only warm winters warm them, to Corrigan, for example, according to the meteorological database, winter in 2016 was one of the warmest ever. As a result, the rats reproduce even in a period when it has not yet been fully established. Produce about once, once and a few times in the threshing floor, to Corrigan, and times and warm winters are likely to take place more often.
The blindness of freezing winters is thus another step towards fulfilling the ideal conditions for the growth of rodent populations. Today, I dare to call New York the world’s Pestropolis, there is one (the problem is English) and the problem will be noticeably more gradual.
that these rodents are more than usual, recorded as the first rodent control companies. In Sttech, the company famous for the liquidation of various PCCs Orkin will record a sharp increase in turnover since 2013. The number of entrances to the terrace, the number of loaded traps and the full range of deratizanch ranges are numerous. Despite this, the rodent evidently does not grow. On an EU-wide average, the number of rodent encounters in households increased by 9 percent in 2015 alone, Orkin said in the press.
In Boston, for example, in 2015, traces of rodents, such as bitten food and dung, were recorded in the household by 25 percent of respondents, 17 percent of whom even caught rodents directly. In cities like Chicago or Philadelphia today, you will see a rat not a pigeon on the street, Corrigan added.
Dangerous roommate
Rats and rats are extremely extreme and highly adaptable species, to Michael Parsons, a professor of biology at the University of Fordham. He points out that for one day in the life of a hundred rodents twenty-eight grams of food and water. And we take the garbage right under their noses. It surprises me. Vte, the day of the wolf among humans has not yet been able to reduce the size of the aunt to the population. But the rats did it once, according to one of the hypotheses about the origin of the plague (see box).
Parsons points out that rodents kill a number of called diseases, which they spread with their saliva, feces and moth. Prim is played by salmonellosis, leptospirosis, bartonellosis, possibly the soul of fever viruses and other hantaviruses.
The problem with pemnoenmi rodents is not limited to food degradation, dreamed environmental hygiene and not the quality of life of the city’s inhabitants. Rats and rats cost the world billions. In 1982, when their sweats were less pronounced now, they globally shared the $ 300 billion code, with the Parsons. For comparison, another global problem, air pollution, is now causing $ 225 billion in global losses.
Codes caused by rodents are not only found in the pub area, but also on the infrastructure. For example, in 2000, rats and rats, gnawing in buildings and under the sidewalks of U.S. cities, drank $ 19 billion in fees. So many pensions were needed for repairs after their standardization. Rodents thus disrupt electrical wiring, the cadon has a number of orders in buildings, according to Parsons.
We don’t know anything about them
The greatest complication is caused by American, but thus by Asian or European rodentologists, the factual illness of any continuous research on rodents. The main question that makes this answer is the average life expectancy of urban rodents.
From laboratory experiments, it can be seen that the female rat should be five and fifty young, depending on the surrounding conditions, and after a lifelessness lasting an average of 22 days, it is able to recover again almost immediately. The whole cycle is thus able to repeat tikrt and estkrt in a year. Her offspring can multiply at msc and pl since his birth.
Tume that it will affect a number of biological factors, but specific data we do not have available, to rodentologist Matthew Combs, who watches over rodents in Manhattan. t toti can one year, but also tyi. And in the urban environment, no one has examined their lives yet.
The same vague idea is about the prevalence of rodent populations with dangerous diseases. It is logical that if the density of rats in the local population is increased, the probability of the occurrence of diseases transmitted by hunters to Combs also increases. We would need space for basic research. A building in which rats or rats go and where we could watch them throughout their existence. Only when someone in the house of a rodent, either think about it or want to eat it right away. With such an approach, we will not learn anything new.
In fact, the company does not even know how many there are out there, sums up the editor Linda Poonov on the CityLab.com server. All in all, New York, Washington DC and Chicago are probably the worst. We have some idea that in the last years, rats have adapted very quickly and developed resistance to most of the applied poisons. But he practically doesn’t take anything else.
Robert Sullivan, who in his book focused on the rat history of American cities, to: I think that rats and rats are a species that reflected the lives of the people in the cities. If cities grow to prosper, rats do not see. When the bag of cities and humans grows up, let the rodents climb to the surface. Their ascension is a signal of our soil.